DNA Osteoporosis Test
$195
Could you be more susceptible to osteoporosis?
Discover your genetic risk for osteoporosis with our at-home DNA Osteoporosis Risk Test. By analyzing key genes involved in bone metabolism, vitamin D activity, and collagen production, our test provides invaluable insights to help you make informed decisions about your bone health journey.
- Uncover Your Bone Health Genetics: Analyze five key genes that play a role in your body's bone strength, cartilage health, and risk for osteoporosis.
- From Vitamin D to Collagen: Learn how your DNA influences your body's ability to use Vitamin D and form collagen, a key building block for bones.
- Proactive Bone Care: By understanding your genetic predisposition, you can make targeted lifestyle changes to support your bone health for years to come.
How it Works

Order your DNA Kit
Place your order online, and we’ll send you a DNA test kit with everything you need to collect your samples.
Collect DNA Samples
Follow the detailed, step-by-step instructions to collect DNA samples using the provided mouth swabs.
Lab Analysis
Use the provided return envelope to mail your DNA samples to our laboratory for analysis.

Receive Results
Download your results from your secure online account as soon as they’re ready.
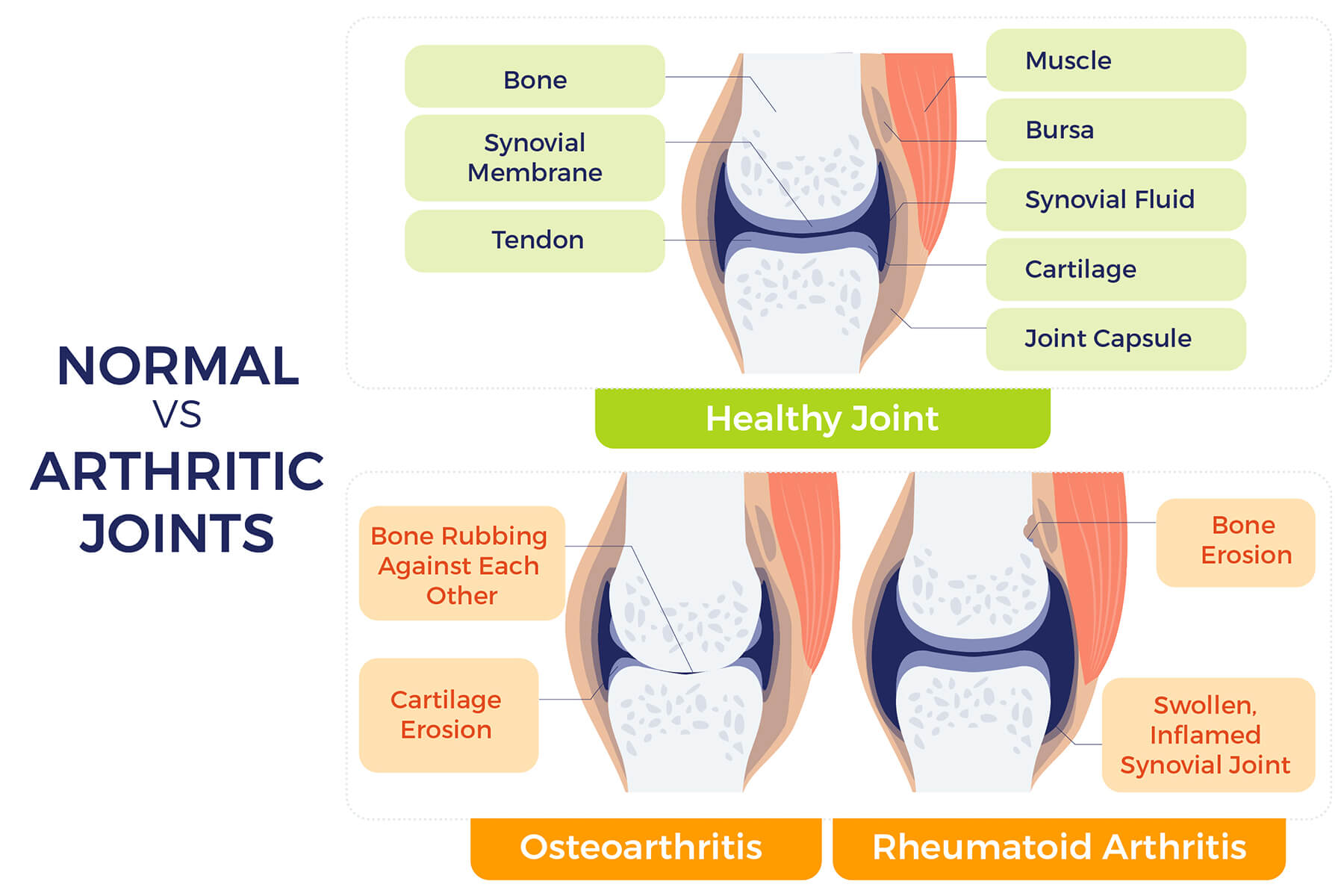
Understanding Bone Health
Strong, healthy bones are essential for support, protection, and overall well-being. Throughout our lives, bones undergo continuous remodeling – old tissue breaks down (resorption) while new bone forms (ossification).
During childhood, adolescence, and early adulthood, new bone production outpaces resorption, allowing peak bone mass around age 30. However, as we age, this balance shifts, and resorption exceeds new bone formation, leading to gradual bone loss.
In many elderly individuals, excessive bone loss results in osteoporosis – a condition of thin, porous, brittle bones with increased fracture risk. Osteoporosis significantly impacts quality of life and healthcare costs, particularly among postmenopausal women experiencing accelerated bone loss due to decreased estrogen.
Osteoarthritis: Another Common Concern
Another prevalent bone and joint issue affecting the elderly is osteoarthritis – the most common form of arthritis. It occurs when protective cartilage within joints wears down, leading to joint pain, stiffness, and inflammation. This condition can severely impair mobility and independence, further highlighting the importance of maintaining bone and joint health throughout life.
Factors Influencing Bone Health
Several modifiable and non-modifiable factors contribute to bone health, including gender, hormone levels, ethnicity, physical activity, medications, nutrient intake, and genetics.
Weight-bearing exercises strengthen bones, while a sedentary lifestyle increases poor bone health risk. A calcium and vitamin D-rich diet is essential, as calcium builds bone tissue and vitamin D aids absorption. Gastrointestinal conditions like Crohn’s, celiac disease, and lactose intolerance can impair nutrient absorption, necessitating proper management and dietary modifications to maintain bone health.
Genetic Variants Analyzed in This Test
Your genes play a crucial role in your bone health, influencing processes like vitamin D metabolism, bone formation, maintenance of bone and joint tissues, and collagen production. Specific gene variations can increase your risk of developing conditions like osteoporosis and osteoarthritis.
- Vitamin D Metabolism: The CYP2R1 and GC genes are essential for activating and transporting vitamin D, which is crucial for calcium absorption and bone health. Variants in these genes can impair these processes, raising your risk of osteoporosis.
- Bone Formation and Maintenance: The WNT16 gene regulates the formation of bone-building cells, while the GDF5 gene oversees the maintenance of bone, joint, and cartilage tissues. Variations in these genes can disrupt these processes, leading to weaker bones and increased risk of fractures and osteoarthritis.
- Collagen and Bone Strength: The COL1A1 gene is responsible for producing a major component of collagen, the protein that provides strength and structure to your bones. Certain variants in this gene can weaken collagen, leading to decreased bone density and increased osteoporosis risk.
Your Genes and Bone Health
This table provides an overview of the key genes and variants included in our At-Home DNA Osteoporosis Risk Test.
| Genes | Variants | Description |
|---|---|---|
| CYP2R1 | rs10741657 | This variant affects the conversion of vitamin D to its active form. Reduced enzyme activity leads to lower levels of active vitamin D, impacting calcium absorption and bone strength. |
| GC | rs4588 | This variant impacts the vitamin D binding protein’s efficiency, affecting vitamin D transport and availability for bone health. |
| WNT16 | rs3801387 | Inactivating variants in this gene disrupt the Wnt signaling pathway, reducing osteoblast formation and bone density, increasing osteoporosis risk. |
| GDF5 | rs143383 | Variants in this gene reduce the expression of the GDF5 protein, essential for bone and joint maintenance, increasing the risk of osteoarthritis and fractures. |
| COL1A1 | rs1800012 | This variant affects the formation of type I collagen, leading to decreased bone mineral density and a higher risk of osteoporosis, particularly in postmenopausal women. |
By understanding your genetic predispositions, you and your healthcare provider can create a personalized plan to optimize your bone health
Frequently Asked Questions
What will I learn from the DNA Osteoporosis Test?
Your genes play a significant role in your overall bone health and your risk of developing osteoporosis. This test analyzes key genetic markers to determine if you have an increased genetic risk, empowering you to make lifestyle changes today to improve your bone strength for the future.
Who should take this test?
This test is valuable for anyone with a family history of osteoporosis or other risk factors, such as a small frame or a history of fractures. It is also for any individual who wants to take a proactive approach to their long-term bone health.
What specific genes does the test analyze?
This test examines five key genes (COL1A1, GDF5, WNT16, GC, and CYP2R1) that are known to play a role in your bone health and risk of osteoporosis. These genes are involved in processes like collagen formation, cartilage health, and Vitamin D metabolism, all of which are critical for strong bones.
Is this test a diagnosis for osteoporosis?
No, this test does not diagnose osteoporosis. It identifies genetic markers that increase your risk. A formal diagnosis of osteoporosis requires a bone mineral density scan (DEXA scan) and consultation with a healthcare provider, who can use your genetic report as part of a comprehensive assessment.
How can the results of this test help me protect my bones?
Finding out you are at an increased genetic risk for osteoporosis allows you to take action today to improve your bone strength. You can use this information to have more informed discussions with your doctor about bone density screening, and to implement targeted lifestyle changes, such as specific exercises and dietary adjustments rich in calcium and Vitamin D, to support your bones long-term.
Is your testing facility reputable and accredited?
How will I receive my results?
How long does it take to get results?
Once your sample is received by our laboratory, processing usually takes 6-8 weeks. You will receive an email notification when your results are ready, and you can access your detailed report through a secure online portal.
Is the testing process confidential?
Yes, your confidentiality is guaranteed. From the discreet packaging of the test kit to the secure delivery of your results, we ensure your privacy is protected every step of the way.